

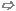
 IR-Drop Analysis
IR-Drop Analysis
Select Power Supply Pin: The button allows the user to select a power pin of a pre-defined power supply device (see Table for Power Supply Modeling).
Power pin: Displays the selected power pin (see Table for Power Supply Modeling). The field can not be edited.
Ground pin: Displays the selected ground pin (see Table for Power Supply Modeling). The field can not be edited.
R-source: Displays the inner resistance of the power/ground pin pair (see Table for Power Supply Modeling). The field can be edited.
V-source: Displays the voltage value of the power/ground pin pair (see Table for Power Supply Modeling). The field can be edited.
Excitations/ports frame

Power Pin: Displays the shifted power pin of an I/O device. The field can not be edited.
Ground Ref: Displays the corresponding ground reference pin of an I/O device (see Power Consumption Modeling) . The field can be edited.
I-DC: Displays the DC current consumption of the power/ground pin pair (see Power Consumption Modeling). The field can be edited.
Element size: Defines the size of the mesh cells.
The Geometry simplification frame includes three further fields (see also Geometry Simplification for PEEC)
Minimum angle for smoothing: Defines the minimum angle
Minimum segment length for smoothing: The values are interpreted with the global units.
Maximum line deviation for smoothing: Specifies the maximal value which the smoothed polygon is allowed to deviate from the original polygon. The values are interpreted with the global units. Setting this parameter to zero means to switch off smoothing.