|
微波射频仿真设计 |
|
|
微波射频仿真设计 |
|
| 首页 >> Ansoft Designer >> Ansoft Designer在线帮助文档 |
|
Nexxim Simulator > Voltage Source, Random Bit Generator
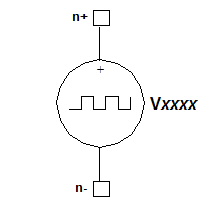 Random Bit Generator Voltage Source Netlist FormatThe format for a pseudorandom bit generator voltage source is: Vxxxx n+ n- [DC=val] RBG[=1] V1=val V2=val [TD=val] TRF=val PW=val [SEED=val] [BITLIST=#bitlist] [BITFILE=file_reference] [TONE=val] [SETDC=val] n+ and n- are the positive and negative nodes.
Bit Generator Voltage Source Netlist ExamplesV23 23 33 RBG V1=0 V2=1.5 TD=1ns TRF=0.5ns PW=1.5ns V43 43 53 RBG V1=0 V2=1.5 TD=1ns TRF=0.5ns PW=1.5ns SEED=1023 V83 83 93 RBG V1=0 V2=1.5 TD=1ns TRF=0.5ns PW=1.5ns + BITLIST=#111100001010110010010110 In the first example (V23), a random bit sequence will be generated, starting from a random seed. In the second example (V43), the random bit sequence starts from the given SEED, and so will be the same each time the simulation is run. In the third example, (V83), the bit sequence specified by the BITLIST parameter will be generated. Notes1. The RBG=1 source is supported only for compatibility with earlier releases. New designs should use the Digital RBG or the Digital Random Bit Generator with Jitter. 2. The RBG source is a time-domain element, suitable primarily for transient analysis simulations. The RBG source can be used in harmonic balance analysis only when a BITLIST is given. See Using the RBG Source in Harmonic Balance for details. 3. The BITLIST argument is ignored when a file_reference is supplied via the BITFILE argument. 4. When no BITLIST or BITFILE argument is supplied, the RBG voltage source generates a pseudorandom bit sequence, starting from a random seed value. When no BITLIST or BITFILE is present, the optional SEED can be used to control the bit sequence. The SEED must be an integer value (the maximum absolute value is the maximum size of integers on your system). Using the same SEED guarantees that the same sequence of bits will be generated on each simulation. 5. When a BITLIST or BITFILE is supplied, the RBG source generates the specified sequence of 0 and 1 bits, and repeats the sequence until simulation terminates. When a BITLIST or BITFILE is present, any SEED value will be ignored. 6. In all cases, the sequence of generated bits starts after the time delay given by TD, and continues until the stop time (tstop) of the transient analysis is reached. Each bit changes state with rise or fall time given by TRF and has the pulse width given by PW 7. If TD is negative, an error occurs and the source is ignored. 8. If TRF is negative or zero, an error occurs and the source is ignored. 9. If PW is negative or zero, an error occurs and the source is ignored. 10. DC Analysis Parameter. The DC parameter specifies the DC magnitude to be applied during a DC operating point analysis. The DC value should be the same as the initial voltage value V1 (DC will be made equal to V1 if they are not equal initially). 11. The parameter BITFILE =file_reference refers to an external file containing the bit data. See File References in the Nexxim netlist File Format topic for details. The format of the VRBG data file is: #bitlist Where bitlist is a sequence of 1’s and 0’s without any whitespace. 12. Using the RBG Source in Harmonic Balance. The RBG VCVS is primarily a time-domain element, best simulated with a time-domain tool such as transient analysis. The RBG source can be used with harmonic balance analysis only when an explicit BITLIST is provided. With a random sequence, the circuit cannot reach a steady state required for harmonic balance. For harmonic balance analysis, one test tone must be a submultiple or equal to the bit-frequency of the voltage source. To ensure that the desired HB frequency is used with a RBG VCVS source, qualify the source by adding a TONE=frequency entry at the end of the instance statement. That frequency also appears as an argument in the .HB statement. The default bit-frequency is: 1/[(PWL + TRF) ´ (number of bits in BITLIST)]
HFSS视频教程 ADS视频教程 CST视频教程 Ansoft Designer 中文教程 |
|
Copyright © 2006 - 2013 微波EDA网, All Rights Reserved 业务联系:mweda@163.com |
|