Boundary Conditions - Phase Shift/Scan Angles
 Simulation:
Settings Simulation:
Settings 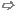 Boundaries Boundaries  Phase Shift/Scan Angles Phase Shift/Scan Angles
This property page allows you to define values for
phase shifts or scan angles for unit cell or periodic boundary conditions.
Note:
These settings are supported by the frequency
domain solver and the eigenmode
solver. For the transient
solver, the values for phase shifts / scan angles must be zero.
If a frequency
domain solver calculation is performed and waveguide
ports share one or two pairs of edges
with periodic boundaries, the phase shift and constant angle of incidence
definitions affect the port modes. For instance, if a constant angle of
incidence is specified, homogeneous ports with periodic boundaries yield
a plane wave propagating along the direction given in spherical coordinates
(theta and phi, see below), and a number of higher-order Floquet modes.
X/Y/Z
Set the phase shift in degrees
for the X, Y or Z direction here. Each field is only editable if a periodic
boundary condition is used for the plane perpendicular to X, Y or Z, respectively.
The fields on the upper periodic boundary condition are then equal to the
fields on the lower periodic boundary condition times the phase factor,
for instance
E( xmin
+ d x) = exp( i d
fx
) E( xmin
),
where d
x > 0 is the spatial lattice period in X direction, and d
fx is the phase shift in X direction.
Scan Angles
This option only applies to the frequency
domain solver.
If activated, you may enter an angle modifying
the phase on the periodic boundaries. The periodic phase shift is changed
across the periodic boundaries according to the phase value of an imaginary
incident plane wave at the boundaries with the angles theta and phi.
Please note that the angles theta and phi refer
to the spherical coordinate system with the z-axis as polar axis. Therefore,
you currently may not enter a constant angle if the periodic boundaries
are located at the zmin/zmax position.
If constant angles are activated, the spherical
coordinate system with the angles theta and phi is displayed in addition
to the structure and boundaries.
Theta
Enter the value for theta in degrees here. Theta
is the angle between the z-axis and the propagation direction of a plane
wave in background material. This option only applies to the frequency
domain solver.
Phi
Enter the value for phi here. Please note that
if the periodic boundaries are located only at the xmin/xmax position
phi is set to 0 degrees automatically. If the periodic boundaries are
located only at the ymin/ymax position phi is automatically set to 90
degrees. This option only applies to the frequency
domain solver.
Outward/Inward
Whether the scan angle Theta,
Phi specifies the direction of
an outgoing or incoming plane wave can be specified here. If the plane
wave propagation vector has a positive z-component, then the Floquet port
at the lower z-boundary has two fundamental modes which correspond to
the outward traveling plane wave in the given direction. The corresponding
port modes at the upper Floquet port boundary however do not represent
the plane wave which is incoming from the same direction. To excite this
plane wave at the upper Floquet port, change the direction to inward.
OK
Accepts your settings and leaves
the dialog box.
Cancel
Closes this dialog box without
performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
See also
Frequency
Domain Solver
Boundary Conditions: Boundaries,
Symmetry
Planes,
Unit Cell,
Boundary
Temperature




HFSS视频教程
ADS视频教程
CST视频教程
Ansoft Designer 中文教程
|