

 Particle Sources
Particle Sources Particle Source on PEC
Particle Source on PEC Thermionic
Thermionic Edit
Edit Particle Sources
Particle Sources Particle Source on any Surface
Particle Source on any Surface Thermionic
Thermionic Edit
Edit Particle Sources
Particle Sources Particle Point Source
Particle Point Source Thermionic
Thermionic Edit
Edit Particle Sources
Particle Sources Particle Circular Source
Particle Circular Source Thermionic
Thermionic Edit
Edit
The Thermionic Emission model is subdivided into two parts:
Space charge emission.
Thermionic emission, based on the Richardson-Dushman equation.
Both emission models are calculated during the emission process. The emission model (SCL or Thermionic) with lowest emission current is finally used for the simulation.
|
Thermionic Emission: The Thermionic Emission model does not calculate an initial momentum for the particles. The initial momentum has to be defined within the "Kinetic Settings" section of this dialog box. pemission = pkinetic setting
Space Charge Limited Emission: The SCL Emission model automatically calculates an initial momentum for the particles. The momentum of the "Kinetic Settings" section is added to the initial momentum of the emission model. pemission = pscl-model + pkinetic setting |
Kinetic settings
Kinetic type
Select the kinetic type for further emission properties such as the Kinetic
Value (see also Kinetic Particle Settings):
Velocity,
Beta,
Gamma,
Normed Momentum,
Energy,
Temperature
Distribution
Select if the kinetic settings should be Maxwellian or uniformly distributed.
Kinetic
value
The kinetic start value of the emitted particles.
See also the Kinetic
Particle Settings page.
Kinetic spread
The energy spread (from 0 to 200 percent) offers the possibility to specify
a randomly calculated emission energy. The kinetic emission type (e.g.
energy, momentum) is calculated uniformly distributed in the range of:
Angle
spread
Determines the maximal deviation between the particle's start angle and
the plane's normal. The emitting angle is randomly chosen within the range
between 0 and the given start angle limit. See also the Kinetic Particle Settings page.
Temperature
The temperature is used to specify the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Distribution
bins
Specifies the number of different
temperature levels within the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Thermionic emission
Temperature
Specifies the temperature of the source's surface.
Work function
Work function (in eV) for the particles from the emitting material into vacuum (band gap between emitter and vacuum). For example, the work function of Tungsten equals 4.54eV.
Richardson constant
Specifies the material constant, i.e. the linear factor of the Richardson-Dushman equation.
Calculate Richardson constant
Determines the material constant depending on the solid state parameters.
Space charge limited emission
Enable additional kinetic settings
Enable the additional settings mentioned above to increase/modify the emission energy.
Emit. potential
The potential of the emitting surface is called emitting potential. If the emitting potential is not one of the predefined potential values, choose "User defined" and enter the potential value under "Emit. potential value".
Ref. potential
Specifies the reference potential (for electron guns usually the anode's potential). If the reference potential is not one of the predefined potential values, choose "User defined" and enter the potential value under "Ref. potential value".
Virtual cathode
Specifies the distance of the emitting surface to the virtual emitting surface. Note that the virtual emitting surface is only considered for Child-Langmuir based space charge limited emission. The value represents a scaling factor which describes the virtual gap distance as a multiple of the maximal emitting mesh cell's diagonal length.

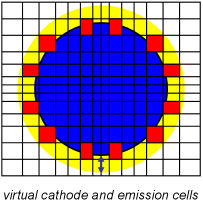
value to enter in the dialog box: dvirtual gap factor
diagmax = max ( diag( emission cells ) )
dvirtual gap = dvirtual gap factor diagmax
Preview
By pressing the Preview button one can get a visualization of the virtual cathode distance:
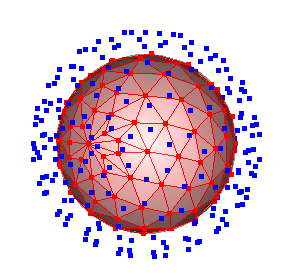
The calculated virtual gap distance in meter is written to the solver log-file.
OK
Confirms the changes and closes the dialog box.
Cancel
Closes this dialog box without performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
See also
Particle Source Definitions, Particle Emission Model Overview, Kinetic Particle Settings