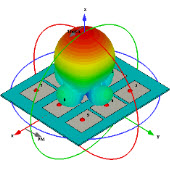
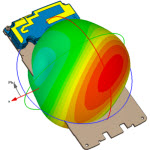
Schneider博士的FDTD示例 C程序
* John B. Schneider
* schneidj@eecs.wsu.edu
*
* Copyright (C) 2003 John B. Schneider
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License
* as published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) version 2
* of the License.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* The license under which this software is publish is available from
* www.fsf.org/copyleft/gpl.html or www.fsf.org/copyleft/gpl.txt.
*
* This code was provided as the solution to a homework problem I
* assigned in EE 417/517 at Washington State University in the Spring
* of 2003. The goal was to write a program which would duplicate, at
* least to a large extend, the patch antenna work described by Sheen
* et al., IEEE Trans. MTT, 38(7):849--857, 1990. HOWEVER, unlike
* Sheen et al., a uniform spatial step is used, thus the geometry
* modeled by this program is not identical to the geometry described
* by Sheen et al. (but it is close). Modifying the code to realize a
* non-uniform grid should not be difficult (and is left as an
* exercise for the reader). Furthermore, a second-order Higdon
* absorbing boundary conditions is used on four of the boundaries of
* the computational domain while a first-order one is used on the
* source-plane wall. (Sheen et al. used a first-order ABC on all of
* the five planes.) This code has in place the arrays to use a
* second-order ABC on the source-plane, but the actual ABC update
* equations are only first-order since they were found to cause fewer
* artifacts when switching between having the source-wall generate
* fields and absorb fields.
*
* This code can be used to model a microstrip line or a microstrip
* patch antenna (the particular problem being modeled is determined
* at compile-time via various declarations). To compile this program
* to model a patch antenna and have each of the ABC turned on at each
* face, use a command such as this:
*
* cc -DPATCH -DABC1 -DABC2 -DABC3 -DABC4 -DABC5 -O sheen_patch.c -o sheen_pa
tch -lm
*
* The switchs control things as follows:
*
* PATCH: If present, the patch is modeled, otherwise a microstrip which
* spans the computational domain.
* ABC1: ABC at the left wall, x=0.
* ABC2: ABC at the far wall, y=LIMY-1.
* ABC3: ABC at the right wall, x=LIMX-1.
* ABC4: ABC at the near wall, y=0.
* ABC5: ABC at the top wall, z=LIMZ-1.
*
* These switches are rather cumbersome but the 417 students in the
* class (i.e., the undergraduates) didn't have to implement ABC's and
* the switches allowed me to use one program for both solutions
* without having to deal with a bunch of if statements. Note that
* the 417 students had to take a "snapshot" of the field at time step
* 300 but I have removed that portion of the code.
*
* Some of the parameters of this code are:
* - Courant number of 1/sqrt(3.1)
* - Computational domain size: 90 x 130 x 20 cells (in x, y, and z
* directions, respectively)
* - del_x = del_y = del_z = 0.265 mm
* - Source plane at y=0
* - Ground plane at z=0
* - Duroid substrate with relative permittivity 2.2. Electric
* field nodes on interface between duroid and freespace use
* average permittivity of media to either side.
* - Substrate 3 cells thick
* - Microstrip 9 cells wide
* - Patch dimensions 47 x 60 cells
*
* As written, this program program runs for 8192 time step and writes
* a single file called "obs-point". If you want the absolute value
* of the S11 parameter for the patch, you will have to run this
* program twice: once with the microstrip and once with patch.
* So, on my Linux system I would issue the following commands:
*
* % cc -DABC1 -DABC2 -DABC3 -DABC4 -DABC5 -O sheen_patch.c -o sheen_patch -l
m
* % sheen_patch
* % mv obs-point obs-point-strip
* % cc -DPATCH -DABC1 -DABC2 -DABC3 -DABC4 -DABC5 -O sheen_patch.c -o sheen_
patch -lm
* % sheen_patch
* % mv obs-point obs-point-patch
*
* Now you can obtain |S11| by subtracting obs-point-strip from
* obs-point-patch to obtain the reflected field. Take the Fourier
* transform of the incident field (i.e., obs-point-strip) and
* incident field, divide on a term by term basis, and plot the
* magnitude of the result. In matlab you would do this with commands
* such as (this can be snipped out and saved to a separate file and
* fed to matlab):
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% These matlab commands can be used to plot the results for the
% Sheen et. simulation.
%
% Note that this assumes a uniform spatial step size of del_s of
% 0.265 mm, a Courant number of 1/sqrt(3.1), and 8192.
% Using those numbers we can find the temporal step size.
%
% c del_t/del_s = 1/sqrt(3.1) => del_t = del_s/(c sqrt(3.1))
% = 5.016996 10^-13
%
% Thus the highest frequency in the simulation is
%
% f_max = 1/(2 del_t) = 9.9661227 10^11
%
% Given that there are 8192 time-steps in the simulation, the spectral
% resolution is
%
% del_f = f_max/(number_of_time_steps / 2) = 243 313 543.8 Hz
%
% Thus del_f is 0.2433 GHz and since we'll plot the spectrum in GHz,
% this is the how we'll scale the horizontal axis for the results from
% the FFT.
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
inc=dlmread('obs-point-strip','\n'); % "incident" field
tot=dlmread('obs-point-patch','\n'); % total field
% reflected field is the difference of total and incident field
ref=tot-inc;
% Take FFT of incident and relected fields. S11 transfer function
% is just reflected divided by incident field. Note that this is
% only meaningful at frequencies where we have sufficient incident
% energy to excite the system, but this should be fine over the range
% of frequencies considered here.
incF=fft(inc);
refF=fft(ref);
freq=0.24331*(0:100);
semilogy(freq(5:80),abs(refF(5:80) ./ incF(5:80)))
title('S11 for patch antenna')
xlabel('Frequency, GHz')
ylabel('|S11|')
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Note that the size of the computational domain is larger than that
* used by Sheen et al., so you may have to be patient while this runs
* (or resize things to suit your needs).
*
* Enjoy!
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* Size of the computational domain. */
#define LIMX 90
#define LIMY 130
#define LIMZ 20
#define HEIGHT 3 /* Number of cells for the dielectric substrate. */
/* Various start and stop point for the feed line and patch. */
#define LINE_X_START 28
#define LINE_X_END 37
#define PATCH_X_START 20
#define PATCH_X_END 67
#define PATCH_Y_START 50
#define PATCH_Y_END 110
/* Parameter to control the width of the Gaussian pulse, which is
rather arbitrary. We just need to ensure we have sufficient
spectral energy at the frequencies of interest. */
#define PPW 30
/* The time at which the source plane switches to being a regular
(absorbing) wall. */
#define SWITCH_SRC 225
#ifndef M_PI
#define M_PI 3.14159265358979323846
#endif
double gaussian(int, double, int);
void init(void);
/* Field arrays */
double ex[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ], ey[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ],
ez[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ], hx[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ],
hy[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ], hz[LIMX][LIMY][LIMZ];
/* I don't like repeated brackets so define some macros to make things
neater. */
#define Ex(I,J,K) ex[I][J][K]
#define Ey(I,J,K) ey[I][J][K]
#define Ez(I,J,K) ez[I][J][K]
#define Hx(I,J,K) hx[I][J][K]
#define Hy(I,J,K) hy[I][J][K]
#define Hz(I,J,K) hz[I][J][K]
/* ABC arrays -- a second-oder Higdon ABC is used at most faces. */
double exfar[LIMX][3][LIMZ][2], ezfar[LIMX][3][LIMZ][2];
#define Exfar(I,J,K,N) exfar[I][J-(LIMY-3)][K][N]
#define Ezfar(I,J,K,N) ezfar[I][J-(LIMY-3)][K][N]
double extop[LIMX][LIMY][3][2], eytop[LIMX][LIMY][3][2];
#define Extop(I,J,K,N) extop[I][J][K-(LIMZ-3)][N]
#define Eytop(I,J,K,N) eytop[I][J][K-(LIMZ-3)][N]
double exnear[LIMX][3][LIMZ][2], eznear[LIMX][3][LIMZ][2];
#define Exnear(I,J,K,N) exnear[I][J][K][N]
#define Eznear(I,J,K,N) eznear[I][J][K][N]
double eyleft[3][LIMY][LIMZ][2], ezleft[3][LIMY][LIMZ][2];
#define Eyleft(I,J,K,N) eyleft[I][J][K][N]
#define Ezleft(I,J,K,N) ezleft[I][J][K][N]
double eyright[3][LIMY][LIMZ][2], ezright[3][LIMY][LIMZ][2];
#define Eyright(I,J,K,N) eyright[I-(LIMX-3)][J][K][N]
#define Ezright(I,J,K,N) ezright[I-(LIMX-3)][J][K][N]
int main() {
double mu0, clight, eps0;
double coefH, coefE0, coefE1, coefE01, holdez, cdtds;
int i, j, k, ii, jj, kk, ntime, ntmax=8192;
/* ABC parameters. */
double c10, c20, c30, c40, c101, c201, c301, c401, c11, c21, c31, c41, temp;
/* output file */
FILE *obs;
obs=fopen("obs-point","w");
mu0=M_PI*4.e-7;
clight=2.99792458e8;
eps0=1.0/(mu0*clight*clight);
/* Run simulation close to Courant limit. */
cdtds = 1./sqrt(3.1);
coefH = cdtds/clight/mu0;
coefE0 = cdtds/clight/eps0;
coefE1 = coefE0/2.2;
coefE01 = coefE0/((1.0+2.2)/2.0);
/* ABC coefficients. */
temp = cdtds;
c10 = -(1.0/temp - 2.0 + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c20 = 2.0*(1.0/temp - temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c30 = 4.0*(1.0/temp + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c40 = (temp-1.0)/(temp+1.0);
temp = cdtds/sqrt((1.0 + 2.2)/2.0);
c101 = -(1.0/temp - 2.0 + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c201 = 2.0*(1.0/temp - temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c301 = 4.0*(1.0/temp + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c401 = (temp-1.0)/(temp+1.0);
temp = cdtds/sqrt(2.2);
c11 = -(1.0/temp - 2.0 + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c21 = 2.0*(1.0/temp - temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c31 = 4.0*(1.0/temp + temp)/(1.0/temp + 2.0 + temp);
c41 = (temp-1.0)/(temp+1.0);
/* Initialize all the fields to zero. */
init();
for (ntime=0; ntime<ntmax; ntime++) {
printf("Working on time step %d ...\n",ntime);
/********** Ex update. *************/
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=1; j<LIMY-1; j++)
for (k=1; k<LIMZ-1; k++)
if (k > HEIGHT)
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE0*((Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i,j-1,k)) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
else if (k == HEIGHT)
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE01*((Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i,j-1,k)) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
else
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE1*((Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i,j-1,k)) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
#ifdef ABC4
if (ntime<SWITCH_SRC) {
#endif
/* Ex nodes on y=0 PMC wall have special updates. */
j=0;
for (i=0;i<LIMX-1;i++)
for (k=1;k<LIMZ-1;k++)
if (k > HEIGHT)
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE0*(2.0*Hz(i,j,k) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
else if (k == HEIGHT)
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE01*(2.0*Hz(i,j,k) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
else
Ex(i,j,k) = Ex(i,j,k) +
coefE1*(2.0*Hz(i,j,k) - (Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i,j,k-1)));
#ifdef ABC4
}
#endif
#ifdef PATCH
/* Zero Ex on metal. */
k=HEIGHT;
/* First the feed strip. */
for (i=LINE_X_START; i<LINE_X_END; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY/2-10; j++)
Ex(i,j,k) = 0.0;
/* Next the patch. */
for (i=PATCH_X_START; i<PATCH_X_END; i++)
for (j=PATCH_Y_START; j<=PATCH_Y_END; j++)
Ex(i,j,k) = 0.0;
#else
/* Zero Ex on metal microstrip. */
k=HEIGHT;
for (i=LINE_X_START; i<LINE_X_END; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
Ex(i,j,k) = 0.0;
#endif
#ifdef ABC2
/* ABC at far wall */
/* Ex above substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=LIMY-1;
for (k=HEIGHT+1; k<LIMZ-1; k++) {
Ex(i,j,k) = c10*(Ex(i,j-2,k)+Exfar(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Exfar(i,j,k,0) + Exfar(i,j-2,k,0) - Ex(i,j-1,k)
- Exfar(i,j-1,k,1)) + c30*Exfar(i,j-1,k,0) - Exfar(i,j-2,k,1);
for(jj=LIMY-3; jj<LIMY; jj++) {
Exfar(i,jj,k,1) = Exfar(i,jj,k,0);
Exfar(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
/* Ex at substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=LIMY-1;
k=HEIGHT;
Ex(i,j,k) = c101*(Ex(i,j-2,k)+Exfar(i,j,k,1))
+ c201*(Exfar(i,j,k,0) + Exfar(i,j-2,k,0) - Ex(i,j-1,k)
- Exfar(i,j-1,k,1)) + c301*Exfar(i,j-1,k,0) - Exfar(i,j-2,k,1);
for(jj=LIMY-3; jj<LIMY; jj++) {
Exfar(i,jj,k,1) = Exfar(i,jj,k,0);
Exfar(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
/* Ex below substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=LIMY-1;
for (k=1; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ex(i,j,k) = c11*(Ex(i,j-2,k)+Exfar(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Exfar(i,j,k,0) + Exfar(i,j-2,k,0) - Ex(i,j-1,k)
- Exfar(i,j-1,k,1)) + c31*Exfar(i,j-1,k,0) - Exfar(i,j-2,k,1);
for(jj=LIMY-3; jj<LIMY; jj++) {
Exfar(i,jj,k,1) = Exfar(i,jj,k,0);
Exfar(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC4
/* ABC at near wall -- only apply ABC after source introduced */
if (ntime >= SWITCH_SRC) {
/* Ex above substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=0;
for (k=HEIGHT+1; k<LIMZ-1; k++) {
Ex(i,j,k) = Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) + c40*(Ex(i,j+1,k)-Ex(i,j,k));
/* Ex(i,j,k) = c10*(Ex(i,j+2,k)+Exnear(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Exnear(i,j,k,0) + Exnear(i,j+2,k,0) - Ex(i,j+1,k)
- Exnear(i,j+1,k,1)) + c30*Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) - Exnear(i,j+2,k,1);
*/
for(jj=2; jj>=0; jj--) {
Exnear(i,jj,k,1) = Exnear(i,jj,k,0);
Exnear(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
/* Ex at substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=0;
k=HEIGHT;
Ex(i,j,k) = Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) + c401*(Ex(i,j+1,k)-Ex(i,j,k));
/* Ex(i,j,k) = c101*(Ex(i,j+2,k)+Exnear(i,j,k,1))
+ c201*(Exnear(i,j,k,0) + Exnear(i,j+2,k,0) - Ex(i,j+1,k)
- Exnear(i,j+1,k,1)) + c301*Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) - Exnear(i,j+2,k,1);
*/
for(jj=2; jj>=0; jj--) {
Exnear(i,jj,k,1) = Exnear(i,jj,k,0);
Exnear(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
/* Ex below substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=0;
for (k=1; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ex(i,j,k) = Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) + c41*(Ex(i,j+1,k)-Ex(i,j,k));
/* Ex(i,j,k) = c11*(Ex(i,j+2,k)+Exnear(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Exnear(i,j,k,0) + Exnear(i,j+2,k,0) - Ex(i,j+1,k)
- Exnear(i,j+1,k,1)) + c31*Exnear(i,j+1,k,0) - Exnear(i,j+2,k,1);
*/
for(jj=2; jj>=0; jj--) {
Exnear(i,jj,k,1) = Exnear(i,jj,k,0);
Exnear(i,jj,k,0) = Ex(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC5
/* ABC at top */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY; j++) {
k=LIMZ-1;
Ex(i,j,k) = c10*(Ex(i,j,k-2)+Extop(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Extop(i,j,k,0) + Extop(i,j,k-2,0) - Ex(i,j,k-1)
- Extop(i,j,k-1,1)) + c30*Extop(i,j,k-1,0) - Extop(i,j,k-2,1);
for(kk=LIMZ-3; kk<LIMZ; kk++) {
Extop(i,j,kk,1) = Extop(i,j,kk,0);
Extop(i,j,kk,0) = Ex(i,j,kk);
}
}
#endif
/*********** Ey update. ***********/
for (i=1; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++)
for (k=1; k<LIMZ-1; k++)
if (k > HEIGHT)
Ey(i,j,k) = Ey(i,j,k) +
coefE0*((Hx(i,j,k)-Hx(i,j,k-1)) - (Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i-1,j,k)));
else if (k == HEIGHT)
Ey(i,j,k) = Ey(i,j,k) +
coefE01*((Hx(i,j,k)-Hx(i,j,k-1)) - (Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i-1,j,k)));
else
Ey(i,j,k) = Ey(i,j,k) +
coefE1*((Hx(i,j,k)-Hx(i,j,k-1)) - (Hz(i,j,k)-Hz(i-1,j,k)));
#ifdef PATCH
/* Zero Ey on metal. */
k=HEIGHT;
/* First the feed strip. */
for (i=LINE_X_START; i<=LINE_X_END; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY/2-10; j++)
Ey(i,j,k) = 0.0;
/* Next the patch. */
for (i=PATCH_X_START; i<=PATCH_X_END; i++)
for (j=PATCH_Y_START; j<PATCH_Y_END; j++)
Ey(i,j,k) = 0.0;
#else
/* Zero Ey on metal microstrip. */
k=HEIGHT;
for (i=LINE_X_START; i<=LINE_X_END; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
Ey(i,j,k) = 0.0;
#endif
#ifdef ABC1
/* ABC on left wall */
/* Ey above substrate */
i = 0;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=HEIGHT+1; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ey(i,j,k) = c10*(Ey(i+2,j,k)+Eyleft(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Eyleft(i,j,k,0) + Eyleft(i+2,j,k,0) - Ey(i+1,j,k)
- Eyleft(i+1,j,k,1)) + c30*Eyleft(i+1,j,k,0) - Eyleft(i+2,j,k,1);
for(ii=0; ii<3; ii++) {
Eyleft(ii,j,k,1) = Eyleft(ii,j,k,0);
Eyleft(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
/* Ey at substrate */
i=0;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
k=HEIGHT;
Ey(i,j,k) = c101*(Ey(i+2,j,k)+Eyleft(i,j,k,1))
+ c201*(Eyleft(i,j,k,0) + Eyleft(i+2,j,k,0) - Ey(i+1,j,k)
- Eyleft(i+1,j,k,1)) + c301*Eyleft(i+1,j,k,0) - Eyleft(i+2,j,k,1);
for(ii=0; ii<3; ii++) {
Eyleft(ii,j,k,1) = Eyleft(ii,j,k,0);
Eyleft(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
/* Ey below substrate */
i=0;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=1; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ey(i,j,k) = c11*(Ey(i+2,j,k)+Eyleft(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Eyleft(i,j,k,0) + Eyleft(i+2,j,k,0) - Ey(i+1,j,k)
- Eyleft(i+1,j,k,1)) + c31*Eyleft(i+1,j,k,0) - Eyleft(i+2,j,k,1);
for(ii=0; ii<3; ii++) {
Eyleft(ii,j,k,1) = Eyleft(ii,j,k,0);
Eyleft(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC3
/* ABC on right wall */
/* Ey above substrate */
i = LIMX-1;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=HEIGHT+1; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ey(i,j,k) = c10*(Ey(i-2,j,k)+Eyright(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Eyright(i,j,k,0) + Eyright(i-2,j,k,0) - Ey(i-1,j,k)
- Eyright(i-1,j,k,1)) + c30*Eyright(i-1,j,k,0) - Eyright(i-2,j,k,1)
;
for(ii=LIMX-3; ii<LIMX; ii++) {
Eyright(ii,j,k,1) = Eyright(ii,j,k,0);
Eyright(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
/* Ey at substrate */
i=LIMX-1;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
k=HEIGHT;
Ey(i,j,k) = c101*(Ey(i-2,j,k)+Eyright(i,j,k,1))
+ c201*(Eyright(i,j,k,0) + Eyright(i-2,j,k,0) - Ey(i-1,j,k)
- Eyright(i-1,j,k,1)) + c301*Eyright(i-1,j,k,0) - Eyright(i-2,j,k,1);
for(ii=LIMX-3; ii<LIMX; ii++) {
Eyright(ii,j,k,1) = Eyright(ii,j,k,0);
Eyright(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
/* Ey below substrate */
i=LIMX-1;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=1; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ey(i,j,k) = c11*(Ey(i-2,j,k)+Eyright(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Eyright(i,j,k,0) + Eyright(i-2,j,k,0) - Ey(i-1,j,k)
- Eyright(i-1,j,k,1)) + c31*Eyright(i-1,j,k,0) - Eyright(i-2,j,k,1)
;
for(ii=LIMX-3; ii<LIMX; ii++) {
Eyright(ii,j,k,1) = Eyright(ii,j,k,0);
Eyright(ii,j,k,0) = Ey(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC5
/* ABC at top */
for (i=0; i<LIMX; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
k=LIMZ-1;
Ey(i,j,k) = c10*(Ey(i,j,k-2)+Eytop(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Eytop(i,j,k,0) + Eytop(i,j,k-2,0) - Ey(i,j,k-1)
- Eytop(i,j,k-1,1)) + c30*Eytop(i,j,k-1,0) - Eytop(i,j,k-2,1);
for(kk=LIMZ-3; kk<LIMZ; kk++) {
Eytop(i,j,kk,1) = Eytop(i,j,kk,0);
Eytop(i,j,kk,0) = Ey(i,j,kk);
}
}
#endif
/************ Ez update. *************/
for (i=1; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=1; j<LIMY-1; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ-1; k++)
if (k > HEIGHT)
Ez(i,j,k) = Ez(i,j,k)
+ coefE0*((Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i-1,j,k)) - (Hx(i,j,k)-Hx(i,j-1,k)));
else
Ez(i,j,k) = Ez(i,j,k)
+ coefE1*((Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i-1,j,k)) - (Hx(i,j,k)-Hx(i,j-1,k)));
#ifdef ABC4
if (ntime<SWITCH_SRC) {
#endif
/* Ez update on "near" wall. */
j = 0;
for (i=1; i<LIMX; i++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ; k++)
if (k > HEIGHT)
Ez(i,j,k) = Ez(i,j,k)
+ coefE0*((Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i-1,j,k)) - 2.0*Hx(i,j,k));
else
Ez(i,j,k) = Ez(i,j,k)
+ coefE1*((Hy(i,j,k)-Hy(i-1,j,k)) - 2.0*Hx(i,j,k));
/* source at y=0 wall of computational domain */
holdez = gaussian(ntime, cdtds, PPW)/3.0;
j=0;
for (i=LINE_X_START; i<=LINE_X_END; i++)
for (k=0; k<HEIGHT; k++)
Ez(i,j,k) = holdez;
/* Ez(i,j,k) = Ez(i,j,k) + holdez; */
#ifdef ABC4
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC1
/* ABC on left wall */
/* Ez above substrate */
i = 0;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=HEIGHT; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c10*(Ez(i+2,j,k)+Ezleft(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Ezleft(i,j,k,0) + Ezleft(i+2,j,k,0) - Ez(i+1,j,k)
- Ezleft(i+1,j,k,1)) + c30*Ezleft(i+1,j,k,0) - Ezleft(i+2,j,k,1);
for(ii=0; ii<3; ii++) {
Ezleft(ii,j,k,1) = Ezleft(ii,j,k,0);
Ezleft(ii,j,k,0) = Ez(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
/* Ez below substrate */
i=0;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=0; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c11*(Ez(i+2,j,k)+Ezleft(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Ezleft(i,j,k,0) + Ezleft(i+2,j,k,0) - Ez(i+1,j,k)
- Ezleft(i+1,j,k,1)) + c31*Ezleft(i+1,j,k,0) - Ezleft(i+2,j,k,1);
for(ii=0; ii<3; ii++) {
Ezleft(ii,j,k,1) = Ezleft(ii,j,k,0);
Ezleft(ii,j,k,0) = Ez(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC2
/* ABC at far wall */
/* Ez above substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=LIMY-1;
for (k=HEIGHT; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c10*(Ez(i,j-2,k)+Ezfar(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Ezfar(i,j,k,0) + Ezfar(i,j-2,k,0) - Ez(i,j-1,k)
- Ezfar(i,j-1,k,1)) + c30*Ezfar(i,j-1,k,0) - Ezfar(i,j-2,k,1);
for(jj=LIMY-3; jj<LIMY; jj++) {
Ezfar(i,jj,k,1) = Ezfar(i,jj,k,0);
Ezfar(i,jj,k,0) = Ez(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
/* Ez below substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=LIMY-1;
for (k=0; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c11*(Ez(i,j-2,k)+Ezfar(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Ezfar(i,j,k,0) + Ezfar(i,j-2,k,0) - Ez(i,j-1,k)
- Ezfar(i,j-1,k,1)) + c31*Ezfar(i,j-1,k,0) - Ezfar(i,j-2,k,1);
for(jj=LIMY-3; jj<LIMY; jj++) {
Ezfar(i,jj,k,1) = Ezfar(i,jj,k,0);
Ezfar(i,jj,k,0) = Ez(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC4
/* ABC at near wall -- only apply after source introduced */
if (ntime >= SWITCH_SRC) {
/* Ez above substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=0;
for (k=HEIGHT; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = Eznear(i,j+1,k,0) + c40*(Ez(i,j+1,k) - Ez(i,j,k));
/* Ez(i,j,k) = c10*(Ez(i,j+2,k)+Eznear(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Eznear(i,j,k,0) + Eznear(i,j+2,k,0) - Ez(i,j+1,k)
- Eznear(i,j+1,k,1)) + c30*Eznear(i,j+1,k,0) - Eznear(i,j+2,k,1);
*/
for(jj=2; jj>=0; jj--) {
Eznear(i,jj,k,1) = Eznear(i,jj,k,0);
Eznear(i,jj,k,0) = Ez(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
/* Ez below substrate */
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++) {
j=0;
for (k=0; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = Eznear(i,j+1,k,0) + c41*(Ez(i,j+1,k) - Ez(i,j,k));
/*
Ez(i,j,k) = c11*(Ez(i,j+2,k)+Eznear(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Eznear(i,j,k,0) + Eznear(i,j+2,k,0) - Ez(i,j+1,k)
- Eznear(i,j+1,k,1)) + c31*Eznear(i,j+1,k,0) - Eznear(i,j+2,k,1);
*/
for(jj=2; jj>=0; jj--) {
Eznear(i,jj,k,1) = Eznear(i,jj,k,0);
Eznear(i,jj,k,0) = Ez(i,jj,k);
}
}
}
}
#endif
#ifdef ABC3
/* ABC on right wall */
/* Ez above substrate */
i = LIMX-1;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=HEIGHT; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c10*(Ez(i-2,j,k)+Ezright(i,j,k,1))
+ c20*(Ezright(i,j,k,0) + Ezright(i-2,j,k,0) - Ez(i-1,j,k)
- Ezright(i-1,j,k,1)) + c30*Ezright(i-1,j,k,0) - Ezright(i-2,j,k,1)
;
for(ii=LIMX-3; ii<LIMX; ii++) {
Ezright(ii,j,k,1) = Ezright(ii,j,k,0);
Ezright(ii,j,k,0) = Ez(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
/* Ez below substrate */
i=LIMX-1;
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++) {
for (k=0; k<HEIGHT; k++) {
Ez(i,j,k) = c11*(Ez(i-2,j,k)+Ezright(i,j,k,1))
+ c21*(Ezright(i,j,k,0) + Ezright(i-2,j,k,0) - Ez(i-1,j,k)
- Ezright(i-1,j,k,1)) + c31*Ezright(i-1,j,k,0) - Ezright(i-2,j,k,1)
;
for(ii=LIMX-3; ii<LIMX; ii++) {
Ezright(ii,j,k,1) = Ezright(ii,j,k,0);
Ezright(ii,j,k,0) = Ez(ii,j,k);
}
}
}
#endif
/************ Hx update. ************/
for (i=0; i<LIMX; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ-1; k++)
Hx(i,j,k) = Hx(i,j,k)
+ coefH*((Ey(i,j,k+1)-Ey(i,j,k)) - (Ez(i,j+1,k)-Ez(i,j,k)));
/************ Hy update. ************/
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ-1; k++)
Hy(i,j,k) = Hy(i,j,k)
+ coefH*((Ez(i+1,j,k)-Ez(i,j,k)) - (Ex(i,j,k+1)-Ex(i,j,k)));
/************ Hz update. ************/
for (i=0; i<LIMX-1; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY-1; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ; k++)
Hz(i,j,k) = Hz(i,j,k)
+ coefH*((Ex(i,j+1,k)-Ex(i,j,k)) - (Ey(i+1,j,k)-Ey(i,j,k)));
fprintf(obs,"%f\n",Ez((LINE_X_START+LINE_X_END)/2,PATCH_Y_START-10,2));
}
fclose(obs);
return 0;
}
/* ------------------------- end of main ------------------------- */
/* ########################## gaussian ########################### */
/* Gaussian pulse.
*/
double gaussian(int ntime, double cdtds, int ippw) {
double arg, time;
time = (double)(ntime);
arg = pow(M_PI*(cdtds*time/(double)(ippw)-1.),2);
/* If the argument is greater than 70.0, the result is so small we
may as well skip calculating the exponential and return zero. */
if (arg > 70.0) {
return 0.0;
} else {
return exp(-arg);
}
}
/* ------------------------ end of gaussian ------------------------ */
/* ########################### init ############################# */
void init() {
int i, j, k;
/* Initialize all fields. */
/* Ex. */
for (k=0;k<LIMZ;k++)
for (j=0;j<LIMY;j++)
for (i=0;i<LIMX;i++)
Ex(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* Ey. */
for (k=0;k<LIMZ;k++)
for (j=0;j<LIMY;j++)
for (i=0;i<LIMX;i++)
Ey(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* Ez. */
for (k=0;k<LIMZ;k++)
for (j=0;j<LIMY;j++)
for (i=0;i<LIMX;i++)
Ez(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* Hx. */
for (k=0;k<LIMZ;k++)
for (j=0;j<LIMY;j++)
for (i=0;i<LIMX;i++)
Hx(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* Hy. */
for (i=0;i<LIMX;i++)
for (j=0;j<LIMY; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ; k++)
Hy(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* Hz. */
for (i=0; i<LIMX; i++)
for (j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
for (k=0; k<LIMZ; k++)
Hz(i,j,k) = 0.;
/* ABC arrays */
for (i=0; i<LIMX; i++)
for(j=LIMY-3; j<LIMY; j++)
for(k=0; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Exfar(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Exfar(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Ezfar(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Ezfar(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Exnear(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Exnear(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Eznear(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Eznear(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
}
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
for(j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
for(k=0; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Eyleft(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Eyleft(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Ezleft(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Ezleft(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
}
for (i=0; i<LIMX; i++)
for(j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
for(k=0; k<3; k++) {
Extop(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Extop(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Eytop(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Eytop(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
}
for (i=LIMX-3; i<LIMX; i++)
for(j=0; j<LIMY; j++)
for(k=0; k<LIMZ; k++) {
Eyright(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Eyright(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
Ezright(i,j,k,0) = 0.0;
Ezright(i,j,k,1) = 0.0;
}
}
/* ------------------------- end of init ------------------------ */
.196
arock大侠,这份程序有没有什么详细些的解释,刚入手,看得比较费劲,如果有,劳烦能不能给我mail一份,多谢了!bentao@163.com
.69
这个程序是关于Sheen的文章的,你可以看看那篇文章。
程序本身结构很简单。主要有些预编译的选项。
自习分析一下程序救治到了。
没有详细的说明。
.126
Sheen哪篇文章啊,题目?劳烦告知!
.69
谢谢ymonkey的回复。
网上FDTD的源程序很多,Schneider博士的FDTD程序也是学生作业,很简单的。
.196
* This code was provided as the solution to a homework problem I
* assigned in EE 417/517 at Washington State University in the Spring
* of 2003. The goal was to write a program which would duplicate, at
* least to a large extend, the patch antenna work described by Sheen
* et al., IEEE Trans. MTT, 38(7):849--857, 1990. HOWEVER, unlike
.126
Application of the Three-Dimensional Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method
to the Analysis of Planar Microstrip Circuits
这个,
可以到这里来看看,
http://www.borg.umn.edu/toyfdtd/ToyFDTD.html
有些例程序,是c或fortran,看看大概思路,计算的大概流程
上面的文章是关于贴片天线的,可以照着做,
振子天线,去看看细导线的网格处理方法
激励看看这个文章吧
On the convergence of common FDTD feed models for antennas
.2
多谢指点了,及时雨啊,刚刚入门,正在摸索,希望以后有机会一起交流:)
.69
这篇文章个人认为可谓经典,俺当初就是认真的将这篇文章上的内容
做了一遍的,感觉收获很大。也自己动手将程序写了一遍作为交给老
的师大作业,只是没有那位老兄写的规范。
.39
相关文章:
- 请问:很多微带线的FDTD参数提取的程序中为何不用PML(05-08)
- 有没有大型稀疏矩阵压缩存贮的子程序?(05-08)
- 急求复数矩阵SVD源程序(05-08)
- 哪里有计算矩量法中sommerfeld积分的程序?(05-08)
- 现在正在编写一个有关波导本征值计算的程序(05-08)
- 求矩量法的金属面散射的源程序(05-08)