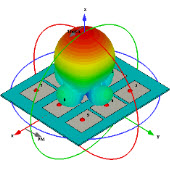
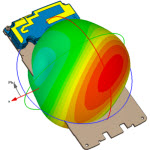
CST仿真天线双站RCS馈电点处加不加波导端口?
希望知道这方面的大神指导一下啊
你需要百度一下,看看天线的结构项RCS和模式项RCS的区别和定义
请学会使用软件的帮助文件。
CST MWS帮助文件《Reference and Normalizing》:
S-Parameter and F-Parameter calculation
In general, S-Parameter results are given as the ratio of incident and reflected voltage wave spectra at a port, where only one port is excited and all others are perfectly matched. Consequently, for transient simulations, all port signals first have to be transformed into the frequency domain, providing broadband results for one port excitation with only one simulation run.
However, in the case of simultaneous excitation several ports are stimulated at once, so it is not possible to apply the general S-Parameter definition. Now the incident and reflected spectra are given as so-called incident and reflected F-Parameters, all normalized to the spectrum of the reference signal. Furthermore, as an additional result and for a better analysis of the structure's behavior, the reflected spectra of all excited ports are normalized to their own incident spectra, respectively, providing so-called active S-Parameters. Since there might be more energy absorbed at a specific port than it itself has injected, the resulting curves could show active behaviour with values greater than one.
Please note that also in the case of a plane wave or field source excitation, the outgoing signals at ports are used to determine F-Parameters as described above.
谢谢,目前还不太会使用帮助文件,只能慢慢学习了
点鼠标的事情能有多难?
Since there might be more energy absorbed at a specific port than it itself has injected, the resulting curves could show active behaviour with values greater than one.
这句话很有道理啊
馈电口不设成 波导口,那就是开路状态,和匹配状态肯定差很多
相关文章:
- cst仿真错误提示,请求帮助 (05-08)
- 关于偶极子天线仿真的问题 (05-08)
- 请问从CST天线仿真结果怎么看出这种天线的极化方式呢? (05-08)
- 哪位大哥用CST仿真过频率选择表面,小弟有问题请教 (05-08)
- CST MWS仿真螺旋天线同轴溃电提示waveguide for port number 1 is too short (05-08)
- CST MWS仿真问题 (05-08)