Technical Notes > Radiated Fields > Array Factors
Theory of the Array Factor Calculation
The composite far-field pattern, Earray (f, q) from an array of N identical radiating sources, each with far-field pattern Eelement (f, q), may be factored into the form
|
|
(1) |
where the "array factor" AF (f, q) is defined as
|
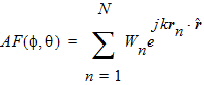
|
(2) |
and where
• (f, q) are the field-point spherical angles.
• Wn
![]() is the complex weight
assigned to element n.
is the complex weight
assigned to element n.
• j ![]() is
is
![]() .
.
• k
![]() is 2p/l.,
wherel is the
wave length in the global material environment.
is 2p/l.,
wherel is the
wave length in the global material environment.
• rn
![]() is
the position vector of element n,
<xn, yn,
zn>.
is
the position vector of element n,
<xn, yn,
zn>.
• ![]()
![]() is the pattern
angle unit vector, <sinqcosf,
sinqsinf,
cosq>.
is the pattern
angle unit vector, <sinqcosf,
sinqsinf,
cosq>.
The complex weights Wn
![]() in
(eq. 2) may be written
in terms of a (real) voltage amplitude An
in
(eq. 2) may be written
in terms of a (real) voltage amplitude An
![]() and
(real) phase
and
(real) phase ![]() as:
as:
|
|
(3) |
To scan a regular array in the direction (f0,
q0),
the element phases ![]() are
set to
are
set to
|
|
(4) |
where
|
|
(5) |
is the scan-angle unit vector.
-

国内最全面的HFSS培训课程,包含7套视频教程和2本教材,资深专家讲解,视频操作演示,结合最新工程案例,让HFSS学习不再难...【详细介绍】





