


A reference block shows no physical behavior, but it is a parametric block that can be referenced by an arbitrary number of blocks (that are not reference blocks themselves). As a result of establishing such a relation, the values of some properties of the referencing block are a copy of the values of the corresponding properties of the reference block, and each modification of a property of the reference block leads to a simultaneous modification of the corresponding property of the referencing block.
In general, the properties of a reference block describe some basic spatial dimensions and material properties related to a certain technology such as Microstrip or Rectangular Waveguide. These common technology properties are always set via a reference block, so you avoid having to specify those properties for each block separately; you need to perform their input only once for the reference block. Note that referencing properties are not editable. If you would like to specify them differently from the properties that they refer to, you must either change the properties of the referenced block or choose another reference block.
Dealing with reference blocks is straightforward. The required settings can be performed within the Block Properties - Parameters for the referencing blocks as well as for the reference blocks:
A reference block can be made the default reference for a specific technology in your design. The property can only be switched off implicitly by making any other block of the same technology the default reference. All blocks of that technology that are added to your design will reference the default reference after their insertion, but previously added blocks are not affected.
If your design contains at least one reference block, you can assign it to a parametric block of the same technology. Since the use of reference blocks is mandatory for blocks belonging to a certain technology, you can only remove a reference block if it is unused. You can always associate a reference for a single block with a different reference block within this dialog box.
Consider a waveguide structure according to the image below. Assuming that the waveguides’ cross-sections are identical for all blocks but different from the default, you would have to specify the properties describing their widths and heights at least four times. In order to avoid such repetitions and speed up your work, CST DESIGN STUDIO™ offers reference blocks.
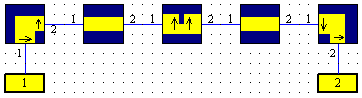
A reference block is inserted into the schematic view in the same manner as any other block. Inside the block selection tree a reference block can be easily identified by a large arrow that is part of its symbol.
After a reference block has been inserted into the schematic view, it becomes the ’default reference’, i.e. all blocks of the same technology that are inserted afterwards refer to that block by default. Of course, you can switch off this functionality as explained below. A design may contain several independent reference blocks.
Let us take a look at the Block Properties - Parameters page of a rectangular waveguide reference block. Insert such a block in an empty schematic view and open its block properties dialog.
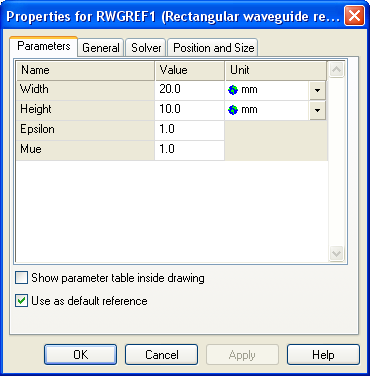
A reference block’s Block Properties - Parameters page differs from the Block Properties - Parameters page of a common block only by the ’Use as default reference’ check box that allows you to switch on its ’Default’ property. Please note that a model always contains exactly one default reference for each technology that is used. Switching on a default reference therefore automatically switches off another one of the same technology. Switching off a default reference is only possible implicitly by switching on another one.
Close the reference block’s dialog and insert a rectangular waveguide block now. Then open its block properties dialog.
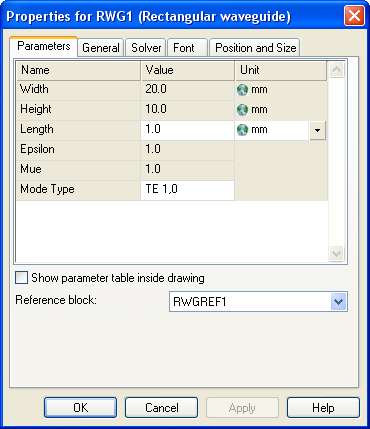
Note that some properties are not editable because their values are determined by the values set for the corresponding properties of the reference block. The rectangular waveguide block was automatically associated with the default reference block.
If there are several reference blocks inside your model you can use the selector box at the bottom of the dialog to choose the appropriate one.
A reference block will be automatically inserted if you insert any block that requires a reference, and no reference of the same technology exists yet. All blocks that are inserted afterward refer to that reference block which defines common parameters in advance (if you do not add another reference).
Note that switching on the ’Default’ property of a reference block does not affect any other block of the existing design, only blocks that will be inserted afterward.
See also