

|
CPU: |
|
|
GPU: |
Extract
from CST PARTICLE STUDIO
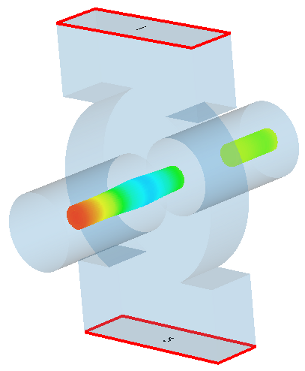
This workflow example demonstrates how to build up the output cavity of a klystron for a PIC simulation. A klystron is a device to amplify microwave and/or radio frequency signals. The output resonator is the last stage (cavity) of a klystron, the amplified signal can be extracted by waveguide ports. Since only the output resonator as a part of the klystron is simulated, a Gaussian emission model is used to define an already bunched particle beam.
CST PARTICLE STUDIO allows you to define the properties of the background material. Anything you do not fill with a particular material will automatically be considered as the background material. For this structure, it is sufficient to model only the vacuum space. The background material will be set to perfect electrical conductor (PEC).
Further information can be obtained from the "Workflow and Solver Overview" documentation.
Beam tube and cylindrical cavity are generated by using two vacuum cylinders (surrounded by PEC background). The waveguide connectors are built with the help of two vacuum bricks.
The particle beam excitation is defined by a circular particle source. At the lower and upper y-boundaries two waveguide ports are defined that monitor and extract the rf-power. Additionally, a constant magnetic field of 0.2 Tesla is defined that is used to prevent the transversal expansion of the beam.
A PIC Position Monitor records the positions, kinetic
quantities and charges of all particles each 0.1 ns. Port signals are
available in Navigation Tree: 1D Results Port signals.
Port signals.
During the simulation, the current position of the
particles can be seen by selecting Navigation
Tree: 2D/3D Results Particles
Particles Particle preview. The position of the
particles can be updated by pressing F5
or by clicking on 2D/3D Plot: Plot Properties
Particle preview. The position of the
particles can be updated by pressing F5
or by clicking on 2D/3D Plot: Plot Properties Update Results.
Update Results.