

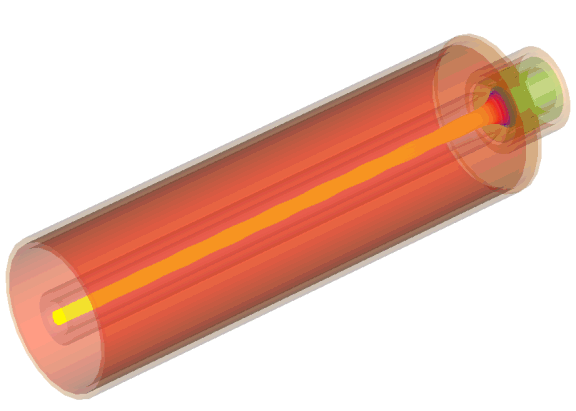
The pierce type gun example demonstrates the analysis of an electrically large gun configuration. The acceleration of the electrons takes place only within a small part of the computational domain, hence nearly 90% of the gun consists of a drift-tube. The acceleration region is located between anode and cathode where the strongest electric field exists. The cathode also acts as guiding electrode and particle source whereas the anode incorporates the drift-tube. The magnetic field is generated by a large current-driven coil and guided by a highly permeable cylinder which encloses the whole configuration.
The gun consists of hollow cylinders forming the magnet-guide, the drift tube, the emitting cathode and the guiding cathode. Loft operations and some intersecting operations with vacuum spheres and cones produces roundings and chamfered and blended edges. The geometric properties of the coils are created by defining two curves, which are defined with the help of the local coordinate system.
Three solvers have to be applied to perform this gun-analysis: The electrostatic and magnetostatic solver calculate the eletrostatic and magnetostatic fields responsible for the external forces pushing the particles. Afterwards the gun-iteration is performed. For the electrostatic calculation, the cathode is assigned to a potential value of 0 V, while the anode carries a potential of 90000 V. The magnetic coil is driven by a current of 5 A with 2000 turns. You might have noticed, that all electrodes consist of perfectly electric conducting materials (PEC), which only affects the electrostatic solver but not for the magnetostatic simulation. The particle source covers the concave face of the cathode and emits the particles. The space charge limited emission model is applied so that particles are emitted as long as the field in the near of the particle surface is larger than zero. The weighting factor of the magnetic field controls the focus of the trajectories inside the drift-tube.
After the gun-iteration has finished, the development
of the emitted current is monitored. The result tree has three new entries:
- magnetic energy
- development of the electric energy
- emitted current and perveance of the particle source over
the iteration cycles