

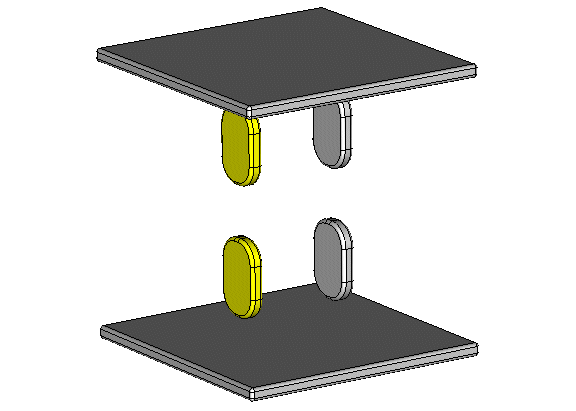
The example shows the approximate equivalence of the behaviour of a highly dielectic material and a floating potential. Compared to dielectric material, floating potential PEC solids can be simulated with less time effort. On two metallic plates, potentials of +1V and -1V are defined. Between these plates there are two solids with a floating potential and two solids of highly dielectric material (relative permittivity 10000). Note that the definition of a floating potential is equivalent to the definition of a zero-charge.
One large plate and one small solid are created by using PEC bricks. The edges of the bricks are blended. The plate and the solids are then copied using the transform/translate function. For the upper two small solids, the material is changed to dielectric.
The large metallic plates carry driving potentials of +1V and -1V respectively. The two small PEC solids are set to floating potential. The example is simulated with a hexahedral and additionally with a tetrahedral mesh. Adaptivity is switched off.
After the calculation, the electric field, the electric flux density and the electric potential can be accessed in the navigation tree under "2D/3D Results". Use the "Draw 3D fields on 2D plane" option to view a 2D potential plot in the YZ-plane at the center of the solids to check the behaviour of the small solids. Each of them has a floating potential that is constant throughout the whole solid.
In addition, two curves are defined to evaluate the fields between the plates. Click on the field of interest and choose "Results->Evaluate Field on Curve" to see the analysis possibilities. XY-plots of the results can be accessed in the navigation tree by selecting subfolders of "1D Results\Field Along Curves".