

 Start Simulation
Start Simulation Specials
Specials Waveguide
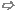
WaveguidePort settings frame
Specifies special waveguide port settings.
Inhomogeneous port accuracy enhancement (QTEM modes): Change here the number of frequency samples for the inhomogeneous port accuracy enhancement. This feature is activated in the Transient Solver Parameters dialog and recalculates the S-parameters with consideration of the broadband frequency behavior of QTEM modes.
Number of frequency samples: The number of frequency samples used for the determination of broadband information of inhomogeneous QTEM port modes.
Consider dielectric losses: This activates the consideration of lossy dielectrics in the port region. The losses are represented by the imaginary part of the permittivity and show a frequency dependence depending on the chosen dispersion model. The losses can have significant influence on the calculated port modes. Note that lossy metals are not supported yet.
Broadband for inhomogeneous waveguide ports (no QTEM modes): Enables the use of a broadband port boundary for inhomogeneously filled waveguide ports. Note that this port operator is designed especially for inhomogeneous waveguides with no QTEM mode propagation, i.e., with only one conductor representing the outer shielding of the port. For an inhomogeneous multiconductor port, please use the accuracy enhancement functionality for QTEM modes.
Number of frequency samples: The number of frequency samples used for the broadband waveguide boundary computation.
Generalized port mode solver: Activate this check button to treat any kind of waveguide port in a generalized framework. This feature will automatically analyze the broadband characteristics of each mode and provide a matched termination at the port plane. Please note that variations of mode fields over frequency are considered in possible excitation and time signal generation.
Line impedance adaptation before solver run: Activates the adaptive port meshing feature to automatically calculate a more accurate line impedance and mode pattern. For this purpose the port mode solver runs several passes while adaptively refining the port mesh.
Accuracy: Represents an accuracy limit for the relative error of the line impedance. The adaptive port meshing is finished when the line impedance has not changed more than this value for two following passes or the maximum number of passes is reached.
Max. number of passes: Restricts the number of passes in the adaptive port meshing if the port line impedance takes too long to converge.
Absorb unconsidered mode fields for inhomogeneous ports: Indicates whether unconsidered mode fields occurring at the waveguide ports should be absorbed by a Mur open boundary or not. This functionality is only active for inhomogeneous ports, where the waveguide operator works less accurately with increasing distance from the mode calculation frequency. This causes slight field errors at the port boundary that are then damped by the Mur operator.
Mode calculation frequency slider: Specifies the frequency that is used for the waveguide port mode calculation. The factor is set between Fmin and Fmax relative to the current frequency range. This slider helps you to improve accuracy at a certain frequency when simulating inhomogeneous ports. This is because the time domain waveguide port operates best at the calculation frequency of the port modes. The defined frequency value is displayed numerically in the corresponding text field.
Note that this setting has no effect on broadband port or full deembedding calculation.
OK
Accepts the input and closes the dialog.
Cancel
Closes this dialog box without performing any further action.
Help
Shows this help text.
See also
Transient Solver Parameters, Frequency range, Signals in Time Domain Simulations Overview
Special Solver Parameters: Steady State, Material, Solver, General