|
微波射频仿真设计 |
|
|
微波射频仿真设计 |
|
| 首页 >> Ansoft Designer >> Ansoft Designer在线帮助文档 |
|
Nexxim Simulator > Transmit JitterTransmit jitter is random variation in the location of edges. QuickEye and VerifEye sources can add the effects of random transmit jitter, in combinations of Gaussian, Uniform, and Periodic jitter. QuickEye Jitter Calculation QuickEye employs a Monte-Carlo method: each transition is displaced a random amount from the nominal time using a probability distribution that combines all specified Gaussian, Uniform, and Periodic jitter distributions. Typically, the Monte Carlo approach requires significantly more effective simulation time, since there needs to be different set of jittered transitions for each bit in the original stream. VerifEye Jitter Calculation VerifEye’s method involves calculating the probability distribution function for edge timings. To handle jitter, VerifEye simply adds a second probability distribution function that combines all specified Gaussian, Uniform, and Periodic jitter distributions. VerifEye applies the jitter probability distribution function to the time-location of each cursor, so that the cursors are not just impulses in voltage, but are spread out due to the Gaussian distribution in time, as shown in Figure 13. 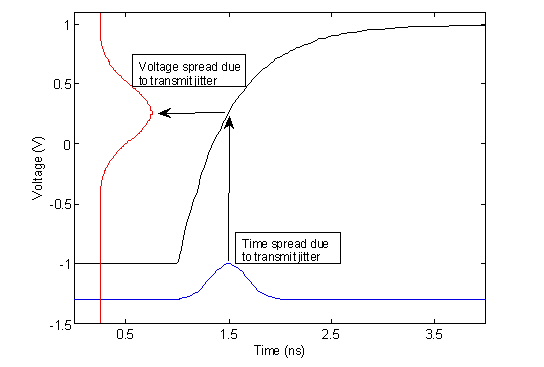 Figure 13: Gaussian random transmit jitter smears out the PDFs for the voltage cursors. Gaussian Transmit Jitter The Gaussian or Normal jitter distribution uses standard deviation σ set by Eye Source entry TXRJ. The Gaussian probability distribution function is:
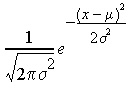
Uniform Transmit Jitter Uniform random jitter represents a distribution of offsets in time from the nominal edge location. The distribution is uniform with bounds set by the TXUJ entry on the Eye Source: -0.5*TXUJ to +0.5*TXUJ Uniform jitter is not common by itself, but can be used in combination with the other jitter distributions to more closely match measured values. Periodic Transmit Jitter Periodic jitter simulates the effect of sinusoidal noise on power supplies. The periodic variation in supply voltage translates into a periodic variation in the location of the edges of the signals generated. In the QuickEye and VerifEye implementation of periodic jitter, the frequency of the periodicity is ignored. The noise frequency is assumed to be uncorrelated to the clock frequency, and so the phase of the periodic noise is basically a uniform random variable. The noise voltage is the sine of this variable, giving the following probability distribution (TXPJ is the Eye Source entry):
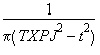
for |t| < TXPJ, zero otherwise. This probability distribution has peaks at |t| = TXPJ, and so is sometimes approximated as a bimodal distribution (but not by QuickEye or VerifEye).
User-Defined Transmit Jitter The user can specify a probability density function (PDF) for transmit jitter, to be added to any other forms of jitter specified in the Eye source for both QuickEye and VerifEye. The PDF data are read from the file indicated by the TXCJ parameter on the Eye source. The data in the jitter file are in two columns. The first column is the time in seconds. The time values may be positive or negative, and need not be centered around t=0. Nexxim automatically centers the mean value of the data at t=0 before doing the jitter calculation. The second column is the PDF value for each time. The PDF values must be greater than or equal to zero. Nexxim automatically scales the PDF data so that the area underneath is unity, so no manual scaling is required. Nexxim performs linear interpolation between the data points. Best results are obtained when the number of data points is large enough to minimize discontinuities of slope. The time axis should extend far enough to allow the PDF to drop to negligible values at both ends. HFSS视频教程 ADS视频教程 CST视频教程 Ansoft Designer 中文教程 |
|
Copyright © 2006 - 2013 微波EDA网, All Rights Reserved 业务联系:mweda@163.com |
|